Introduction
Libertarianism (from French: libertaire, itself from the Latin: libertas, lit. 'freedom') is a political philosophy that upholds liberty as a core value. Libertarians seek to maximize autonomy and political freedom, emphasizing equality before the law and civil rights to freedom of association, freedom of speech, freedom of thought and freedom of choice. Libertarians are often skeptical of or opposed to authority, state power, warfare, militarism and nationalism, but some libertarians diverge on the scope of their opposition to existing economic and political systems. Various schools of libertarian thought offer a range of views regarding the legitimate functions of state and private power. Different categorizations have been used to distinguish various forms of Libertarianism. Scholars distinguish libertarian views on the nature of property and capital, usually along left–right or socialist–capitalist lines. Libertarians of various schools were influenced by liberal ideas.
In the mid-19th century, libertarianism originated as a form of left-wing politics such as anti-authoritarian and anti-state socialists like anarchists, especially social anarchists, but more generally libertarian communists/Marxists and libertarian socialists. These libertarians sought to abolish capitalism and private ownership of the means of production, or else to restrict their purview or effects to usufruct property norms, in favor of common or cooperative ownership and management, viewing private property in the means of production as a barrier to freedom and liberty. While all libertarians support some level of individual rights, left-libertarians differ by supporting an egalitarian redistribution of natural resources. Left-libertarian ideologies include anarchist schools of thought, alongside many other anti-paternalist and New Left schools of thought centered around economic egalitarianism as well as geolibertarianism, green politics, market-oriented left-libertarianism and the Steiner–Vallentyne school. After the fall of the Soviet Union, libertarian socialism grew in popularity and influence as part of anti-war, anti-capitalist and anti- and alter-globalisation movements. (Full article...)
Selected article
Classical liberalism is a political philosophy committed to the ideal of limited government and liberty of individuals, including freedom of religion, speech, press, assembly and free markets.
Classical liberalism developed in the 19th century in Western Europe and the Americas. Although classical liberalism built on ideas that had already developed by the end of the 18th century, it advocated a specific kind of society, government and public policy required as a result of the Industrial Revolution and urbanization. Notable individuals who have contributed to classical liberalism include Jean-Baptiste Say, Thomas Malthus and David Ricardo. It drew on the economics of Adam Smith, a psychological understanding of individual liberty, natural law and utilitarianism and a belief in progress. Classical liberals established political parties that were called "Liberal", although in the United States classical liberalism came to dominate both existing major political parties. There was a revival of interest in classical liberalism in the 20th century led by Friedrich Hayek and Milton Friedman.
In the late 19th century, classical liberalism developed into neo-classical liberalism, which argued for government to be as small as possible in order to allow the exercise of individual freedom. In its most extreme form, it advocated social Darwinism. Right-libertarianism is a modern form of neo-classical liberalism. The term "classical liberalism" was applied in retrospect to distinguish earlier 19th-century liberalism from the newer social liberalism. Classical liberalism is also sometimes used to refer to all forms of liberalism before the 20th century whereas some American conservatives and libertarians use it to describe their belief in the primacy of economic freedom and minimal government. However, it is not always clear which meaning is intended.
Selected quote
| “ | I remember the occasion when a fellow graduate student at Columbia from Sweden wanted to take me downtown to a restaurant for a Swedish meal and introduced me to the Swedish drink aquavit. This was a restaurant at which this Swedish fellow had been getting aquavit all during Prohibition; they had been selling it to him. And this was just after the repeal of Prohibition. We went there and he asked them for some aquavit. They said, "Oh, no, we haven't gotten our license yet." And finally, he talked to them in Swedish and persuaded them to take us into the back where they gave us a glass of aquavit apiece. Now that shows the absurdity of it.
Prohibition was repealed in 1933 when I was 21 years old, so was a teenager during most of Prohibition. Alcohol was readily available. Bootlegging was common. Any idea that alcohol prohibition was keeping people from drinking was absurd. There were speakeasies all over the place. But more than that. We had this spectacle of Al Capone, of the hijackings, of the gang wars... Anybody with two eyes could see that this was a bad deal, that you were doing more harm than good. In addition, I became an economist. And as an economist, I came to recognize the importance of markets and of free choice and of consumer sovereignty and came to discover the harm that was done when you interfered with them. The laws against drugs were passed in 1914, but there was no very great enforcement of it. |
” |
| — Milton Friedman (1912–2006) America's Drug Forum (1991) |
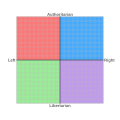
Selected picture
 |
General images
Selected biography -

Steven Wynn "Steve" Kubby (December 28, 1946 – November 20, 2022) was a Libertarian Party activist who played a key role in the drafting and passage of California Proposition 215. The proposition was a ballot initiative to legalize medical marijuana which was approved by voters in 1996. Kubby was known as a cancer patient who relied on medical cannabis.
Kubby authored two books on drug policy reform: The Politics of Consciousness (1995) and Why Marijuana Should Be Legal (2003). He was the Libertarian Party of California candidate for Governor of California in 1998, receiving 0.9% of the vote. In 2008, he declared his candidacy for the Libertarian Party's 2008 presidential nomination and received significant support for the nomination, but was eliminated after the second ballot. (Full article...)Related portals
Parent portals
Socio-political portals
Topics
Categories
Points of interest
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus


























Recent Comments