How Can We Help?
The ischial spine is part of the posterior border of the body of the ischium bone of the pelvis. It is a thin and pointed triangular eminence, more or less elongated in different subjects.
Structure
| Part | Attachment |
|---|---|
| external surface | gemellus superior muscle[1] |
| internal surface | coccygeus muscle,[2] levator ani muscle, pelvic fascia |
| pointed extremity | sacrospinous ligament |
The pudendal nerve travels close to the ischial spine.[3]
Clinical significance
The ischial spine can serve as a landmark in pudendal anesthesia, as the pudendal nerve lies close to the ischial spine.[3][4]
Additional images
-
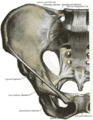
Right hip bone, external surface, showing the greater and lesser sciatic notches, separated by the ischial spine
-
Articulations of pelvis. Anterior view.
-
Pelvis. Anterior view.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 235 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 235 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (2011-01-01), Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (eds.), "Chapter 12 - The hip", Clinical Application of Neuromuscular Techniques, Volume 2 (Second Edition), Oxford: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 391–445, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06815-7.00012-7, ISBN 978-0-443-06815-7, retrieved 2021-02-19
- ^ Bharucha, ADIL E.; Klingele, CHRISTOPHER J. (2005-01-01), Dyck, Peter J.; Thomas, P. K. (eds.), "Chapter 13 - Autonomic and Somatic Systems to the Anorectum and Pelvic Floor", Peripheral Neuropathy (Fourth Edition), Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 279–298, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7216-9491-7.50016-8, ISBN 978-0-7216-9491-7, retrieved 2021-02-19
- ^ a b Christo, Paul J.; Hobelmann, Greg (2009-01-01), Smith, HOWARD S. (ed.), "Chapter 29 - PELVIC PAIN", Current Therapy in Pain, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 216–227, doi:10.1016/b978-1-4160-4836-7.00029-8, ISBN 978-1-4160-4836-7, retrieved 2021-02-19
- ^ "Clinical Case - Perineum & External Genitalia". Archived from the original on 2011-07-17. Retrieved 2009-05-27.




Recent Comments