Coproporphyrinogen III is a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of many compounds that are critical for living organisms, such as hemoglobin and chlorophyll. It is a colorless solid.
The compound is a porphyrinogen, a class of compounds characterized by a hexahydroporphine core with various side chains. The coproporphyrinogens have the outermost hydrogen atoms of the core replaced by four methyl groups −CH3 (M) and four propionic acid groups −CH2−CH2−COOH (P). In coproporphyrogen III, the order around the outer ring is MP-MP-MP-PM. For comparison, coproporphyrinogen I has them in the sequence MP-MP-MP-MP. heme.
Biosynthesis and metabolism
In the main porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, coproporphyrinogen III is derived from uroporphyrinogen III by the action of the enzyme uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase:
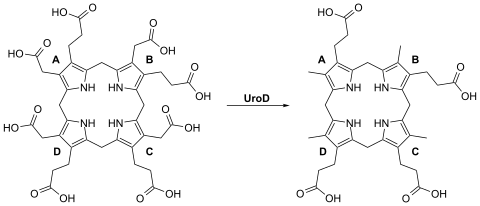
The conversion entails four decarboxylations, which turn the four acetic acid groups −CH2−COOH into methyl groups −CH3, with release of four carbon dioxide molecules.[1][2]
Coproporphyrinogen III is further used as a substrate for the enzyme coproporphyrinogen III oxidase which oxidizes and further decarboxylates it to protoporphyrinogen IX.
References
- ^ Paul R. Ortiz de Montellano (2008). "Hemes in Biology". Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470048672.wecb221. ISBN 978-0470048672.
- ^ Sassa, S.; Kappas, A. (2000). "Molecular aspects of the inherited porphyrias". Journal of Internal Medicine. 247 (2): 169–78. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2796.2000.00618.x. PMID 10692079. S2CID 36820694.


Recent Comments