Bufadienolide is a chemical compound with steroid structure. Its derivatives are collectively known as bufadienolides, including many in the form of bufadienolide glycosides (bufadienolides that contain structural groups derived from sugars). These are a type of cardiac glycoside, the other being the cardenolide glycosides. Both bufadienolides and their glycosides are toxic; specifically, they can cause an atrioventricular block, bradycardia (slow heartbeat), ventricular tachycardia (a type of rapid heartbeat), and possibly lethal cardiac arrest.[1]
Etymology
The term derives from the toad genus Bufo that contains bufadienolide glycosides, the suffix -adien- that refers to the two double bonds in the lactone ring, and the ending -olide that denotes the lactone structure. Consequently, related structures with only one double bond are called bufenolides,[2] and the saturated equivalent is bufanolide.[3]
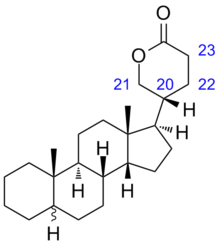
Classification
According to MeSH, bufadienolides and bufanolides are classified as follows:[4][5]
- Polycyclic compounds
- Steroids
- Cardanolides
- Cardiac glycosides
- Bufanolides (includes bufenolides, bufadienolides, bufatrienolides)
- Cardenolides
- Cardiac glycosides
- Cardanolides
- Steroids
References
- ^ Mutschler, Ernst; Schäfer-Korting, Monika (2001). Arzneimittelwirkungen (in German) (8 ed.). Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft. pp. 534, 538. ISBN 3-8047-1763-2.
- ^ Glitsch, H. G.; Pusch, H.; Zylka, Ch. (1990). "The action of 22,23-dihydrobufalin and other cardioactive steroids on contraction and active sodium/potassium transport of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 342 (5): 598–604. doi:10.1007/BF00169051. PMID 2090954. S2CID 21474014.
- ^ IUPAC Recommendations 1999: Revised Section F: Natural Products and Related Compounds
- ^ Bufadienolides at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ^ Cardenolides at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
Further reading
- Steyn, PS; Heerden, FR van (1998). Bufadienolides of plant and animal origin, Natural Product Reports, 15(4):397-413.


Recent Comments