Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 19 April 2015,[1] with advance voting taking place from 8 to 14 April.[2] The 200 members of the Parliament of Finland were elected with the proportional D'Hondt method.
There were 4,463,333 people entitled to vote in Finland and abroad.[3]
Background
Previous government coalition

The incumbent government was a four-party coalition composed of the National Coalition Party, Social Democratic Party, Swedish People's Party and the Christian Democrats as well as independent Member of Parliament Elisabeth Nauclér. The Left Alliance and the Green League were initially also part of the governing coalition, but both left in 2014.
On 22 June 2011, the parliament elected Jyrki Katainen as prime minister by a vote of 118–72; two Left Alliance MPs voted against Katainen, for which they were formally reprimanded by the Left Alliance parliamentary group. They were subsequently expelled from the group, reducing the government majority from 126 MPs to 124. In March 2014 the Left Alliance announced that it was leaving the cabinet, citing the party's opposition to budget cuts in social welfare programs, which had been agreed to by the other five parties.[4] This reduced the government's majority to 112 MPs.
In April 2014 Jyrki Katainen announced that he would not seek another term as the chairman of the National Coalition Party. The NCP chose Alexander Stubb as its new chairman in June, and he subsequently became the new Prime Minister. In September 2014 the Green League announced that it was leaving the cabinet. The Greens were opposed to the other governing parties' decision to grant Fennovoima a licence for building a nuclear power plant in Pyhäjoki.[5] The Greens' departure cut the government's majority to 102 MPs (including the Speaker of the Parliament, who does not vote).[6]
Electoral district changes

In 2013 the parliament decided to merge certain electoral districts to create larger districts: the electoral districts of Northern Savonia and North Karelia were merged into a new district called Savonia-Karelia, while the electoral districts of Kymi and Southern Savonia were merged into a new district called South-Eastern Finland.[7]
| Electoral district | Seats |
|---|---|
| 01 Helsinki | 22 |
| 02 Uusimaa | 35 |
| 03 Finland Proper | 17 |
| 04 Satakunta | 8 |
| 05 Åland | 1 |
| 06 Tavastia | 14 |
| 07 Pirkanmaa | 19 |
| 08 South-East Finland | 17 |
| 09 Savonia-Karelia | 16 |
| 10 Vaasa | 16 |
| 11 Central Finland | 10 |
| 12 Oulu | 18 |
| 13 Lapland | 7 |
Opinion polls

Results

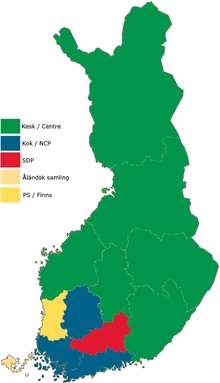
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
| Centre Party | 626,218 | 21.10 | 49 | +14 | |
| Finns Party | 524,054 | 17.65 | 38 | −1 | |
| National Coalition Party | 540,212 | 18.20 | 37 | −7 | |
| Social Democratic Party | 490,102 | 16.51 | 34 | −8 | |
| Green League | 253,102 | 8.53 | 15 | +5 | |
| Left Alliance | 211,702 | 7.13 | 12 | −2 | |
| Swedish People's Party | 144,802 | 4.88 | 9 | 0 | |
| Christian Democrats | 105,134 | 3.54 | 5 | −1 | |
| Pirate Party | 25,086 | 0.85 | 0 | 0 | |
| Independence Party | 13,638 | 0.46 | 0 | 0 | |
| Åland Coalition 2015 (C–M–S) | 10,910 | 0.37 | 1 | 0 | |
| Communist Party | 7,529 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | |
| Change 2011 | 7,442 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pirkanmaa Joint List | 2,469 | 0.08 | 0 | New | |
| Liberals for Åland | 1,277 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | |
| Communist Workers' Party | 1,103 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | |
| Workers' Party | 984 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | |
| For the Poor | 623 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | |
| Independents | 2,075 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 2,968,462 | 100.00 | 200 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 2,968,462 | 99.48 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 15,397 | 0.52 | |||
| Total votes | 2,983,859 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 4,463,333 | 66.85 | |||
| Source: Ministry of Justice, YLE | |||||
Government formation
As the leader of the largest party, Juha Sipilä of Centre was tasked with forming the new government coalition. In early May, Sipilä announced that he would seek to form a right-leaning majority coalition consisting of the three largest parties—the Centre Party, the Finns Party and the National Coalition Party.[9] The coalition negotiations were successful and led to the formation of the Sipilä cabinet on 29 May.
References
- ^ "Finnish Parliamentary Elections 2015" (PDF). vaalit.fi. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 April 2015. Retrieved 18 April 2015.
- ^ "Advance voting begins ahead of parliamentary elections". yle.fi. Yle News English. 8 April 2015. Retrieved 18 April 2015.
- ^ "People entitled to vote". vaalit.fi. Retrieved 18 April 2015.
- ^ Vasemmistoliitto lähtee hallituksesta YLE, 25 March 2014, accessed 18 September 2014.
- ^ Fennovoiman periaatepäätös hyväksyttiin, vihreät jättää hallituksen Helsingin Sanomat, 18 September 2014, accessed 18 September 2014.
- ^ Vihreät ulos hallituksesta – "Mieli on raskas ja pettynyt" YLE, 18 September 2014, accessed 18 September 2014.
- ^ Vaalipiiriuudistus lyötiin lukkoon eduskunnassa YLE, 6 March 2013, accessed 18 September 2014.
- ^ "Yle Tulos palvelu Koko maa". Yle Vaalikone.
- ^ Sipilä opts for right-leaning government, YLE News 7 May 2015, accessed 7 May 2015.
External links
![]() Media related to Parliamentary elections in Finland, 2015 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Parliamentary elections in Finland, 2015 at Wikimedia Commons


Recent Comments