Manganese(II) acetate are chemical compounds with the formula Mn(CH3CO2)2·(H2O)n where n = 0, 2, 4. These materials are white or pale pink solids. Some of these compounds are used as a catalyst and as fertilizer.[3]
Preparation
Manganese(II) acetate can be formed by treating either manganese(II,III) oxide or manganese(II) carbonate with acetic acid:[4]
- Mn3O4 + 2 CH3CO2H → Mn(CH3CO2)2 + Mn2O3 + H2O
- MnCO3 + 2 CH3CO2H → Mn(CH3CO2)2 + CO2 + H2O
Structure
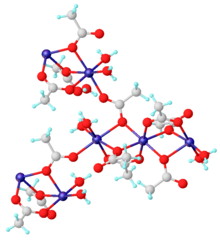
The anhydrous material and dihydrate Mn(CH3CO2)2·2H2O are coordination polymers. The dihydrate has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. Each Mn(II) center is surrounded by six oxygen centers provided by aquo ligands and acetates.
References
- ^ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 3–354, 4–68, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ^ "Manganese compounds (as Mn)". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Thomas Scott; Mary Eagleson (1994), Concise Encyclopedia Chemistry, Walter de Gruyter, p. 620, ISBN 3-11-011451-8, retrieved 2009-07-20
- ^ Arno H. Reidies (2002). "Manganese Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_123. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ Chih-Yi Cheng; Sue-Lein Wang (1991). "Structure of manganese acetate dihydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 47 (8): 1734. doi:10.1107/S0108270191002202.


Recent Comments