The North America Portal
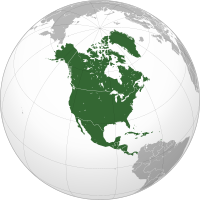
North America is a continent in the Northern and Western Hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes the Bahamas, Bermuda, Canada, the Caribbean, Central America, Clipperton Island, Greenland, Mexico, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Turks and Caicos Islands, and the United States.
North America covers an area of about 24,709,000 square kilometers (9,540,000 square miles), representing approximately 16.5% of the Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In human geography, the terms "North America" and "North American" sometimes refer to just Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Greenland.
It is unknown with certainty how and when first human populations first reached North America. People were known to live in the Americas at least 20,000 years ago, but various evidence points to possibly earlier dates. The Paleo-Indian period in North America followed the Last Glacial Period, and lasted until about 10,000 years ago when the Archaic period began. The classic stage followed the Archaic period, and lasted from approximately the 6th to 13th centuries. Beginning in 1000 AD, the Norse were the first Europeans to begin exploring and ultimately colonizing areas of North America.
In 1492, the exploratory voyages of Christopher Columbus led to a transatlantic exchange, including migrations of European settlers during the Age of Discovery and the early modern period. Present-day cultural and ethnic patterns reflect interactions between European colonists, indigenous peoples, enslaved Africans, immigrants from Europe, Asia, and descendants of these respective groups. (Full article...)
Nahuatl (English: /ˈnɑːwɑːtəl/ NAH-wah-təl; Nahuatl pronunciation: [ˈnaːwat͡ɬ] ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about 1.7 million Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller populations in the United States.
Nahuatl has been spoken in central Mexico since at least the seventh century CE. It was the language of the Mexica, who dominated what is now central Mexico during the Late Postclassic period of Mesoamerican history. During the centuries preceding the Spanish and Tlaxcalan conquest of the Aztec Empire, the Aztecs had expanded to incorporate a large part of central Mexico. Their influence caused the variety of Nahuatl spoken by the residents of Tenochtitlan to become a prestige language in Mesoamerica. (Full article...)
Harold Adams Innis FRSC (November 5, 1894 – November 8, 1952) was a Canadian professor of political economy at the University of Toronto and the author of seminal works on media, communication theory, and Canadian economic history. He helped develop the staples thesis, which holds that Canada's culture, political history, and economy have been decisively influenced by the exploitation and export of a series of "staples" such as fur, fish, lumber, wheat, mined metals, and coal. The staple thesis dominated economic history in Canada from the 1930s to 1960s, and continues to be a fundamental part of the Canadian political economic tradition.
Innis's writings on communication explore the role of media in shaping the culture and development of civilizations. He argued, for example, that a balance between oral and written forms of communication contributed to the flourishing of Greek civilization in the 5th century BC. He warned, however, that Western civilization is now imperiled by powerful, advertising-driven media obsessed by "present-mindedness" and the "continuous, systematic, ruthless destruction of elements of permanence essential to cultural activity." His intellectual bond with Eric A. Havelock formed the foundations of the Toronto School of communication theory, which provided a source of inspiration for future members of the school Marshall McLuhan and Edmund Snow Carpenter. (Full article...)Mount Adams, known by some Native American tribes as Pahto or Klickitat, is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Cascade Range. Although Adams has not erupted in more than 1,000 years, it is not considered extinct. It is the second-highest mountain in Washington, after Mount Rainier.
Adams, named for President John Adams, is a member of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, and is one of the arc's largest volcanoes, located in a remote wilderness approximately 34 miles (55 km) east of Mount St. Helens. The Mount Adams Wilderness consists of the upper and western part of the volcano's cone. The eastern side of the mountain is designated as part of the territory of the Yakama Nation. (Full article...)Did you know...
- ...that the Cuban night lizard is less than 4 cm long and lives exclusively in the west corner of the southern-most coast of Cuba?
- ... that tequila was first produced in the 16th century?
- ...that the word hurricane, used in the North Atlantic and Northeast Pacific, is derived from a native Caribbean Amerindian storm god, Huracan, via Spanish huracán?
- ... that the First Mexican Empire was the official name of independent Mexico under a monarchical regime from 1822 to 1823?
- ...that Jacob Piatt Dunn in 1886 wrote the first scholarly history concerning the Indian Wars?
Selected panorama

Topics
Categories
List articles
Related portals
Northern America
Central America
Caribbean
WikiProjects
 North America
North America-
 Canada
Canada -
 Greenland
Greenland -
 Mexico
Mexico -
 Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon -
 United States
United States  Central America
Central America-
 Belize
Belize -
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica -
 El Salvador
El Salvador -
 Guatemala
Guatemala -
 Honduras
Honduras -
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua -
 Panama
Panama  Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica Caribbean
Caribbean-
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda -
 Bahamas
Bahamas -
 Barbados
Barbados -
 Bermuda
Bermuda -
 Cuba
Cuba -
 Dominica
Dominica -
 Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic -
 Grenada
Grenada -
 Haiti
Haiti -
 Jamaica
Jamaica -
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico -
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis -
 Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia -
 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines -
 Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus




















Recent Comments