
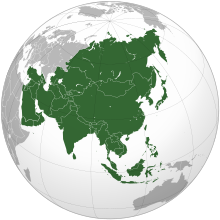
 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured articleDuring World War II, Allied forces conducted air raids on Japan from 1942 to 1945, causing extensive destruction to the country's cities and killing between 241,000 and 900,000 people. During the first years of the Pacific War these attacks were limited to the Doolittle Raid in April 1942 and small-scale raids on military positions in the Kuril Islands from mid-1943. Strategic bombing raids began in June 1944 and continued until the end of the war in August 1945. Allied naval and land-based tactical air units also attacked Japan during 1945. The United States Army Air Forces campaign against Japan began in earnest in mid-1944 and intensified during the war's last months. While plans for attacks on Japan had been prepared prior to the Pacific War, these could not begin until the long-range Boeing B-29 Superfortress bomber was ready for combat. From June 1944 until January 1945, B-29s stationed in India staged through bases in China to make a series of nine raids on targets in western Japan, but this effort proved ineffective. The strategic bombing campaign was greatly expanded from November 1944 when bases in the Mariana Islands became available as a result of the Mariana Islands Campaign. Initial attempts to target industrial facilities using high-altitude daylight "precision" bombing were largely ineffective. From February 1945, the bombers switched to low-altitude night firebombing against urban areas as much of the manufacturing process was carried out in small workshops and private homes: this approach resulted in large-scale urban damage and high civilian casualties. Aircraft flying from Allied aircraft carriers and the Ryukyu Islands also frequently struck targets in Japan during 1945 in preparation for the planned invasion of Japan scheduled for October 1945. During early August 1945, the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki were struck and mostly destroyed by atomic bombs. (Full article...)Selected Country Japan is an island country in East Asia, located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asian mainland. It is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and thousands of smaller islands, covering around 380,000 square kilometres (150,000 sq mi). With a population of more than 125 million as of 2020, Japan is the 11th most populous country. Tokyo is its capital and largest city. Japan is divided into 47 administrative prefectures and eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of the country's terrain is mountainous and heavily forested, concentrating its agriculture and highly urbanized population along its eastern coastal plains. Greater Tokyo is the world's most populous metropolitan area, with more than 38 million inhabitants as of 2016. Part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, Japan's islands are prone to destructive earthquakes and tsunamis. (Full article...)Featured biographyAbū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Ṭalḥa al-Muwaffaq (Arabic: أبو العباس أحمد بن طلحة الموفق), 853/4 or 860/1 – 5 April 902, better known by his regnal name al-Muʿtaḍid bi-llāh (Arabic: المعتضد بالله, "Seeking Support in God"), was the caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate from 892 until his death in 902. Al-Mu'tadid was the son of al-Muwaffaq, who was the regent and effective ruler of the Abbasid state during the reign of his brother, Caliph al-Mu'tamid. As a prince, the future al-Mu'tadid served under his father during various military campaigns, most notably in the suppression of the Zanj Rebellion, in which he played a major role. When al-Muwaffaq died in June 891 al-Mu'tadid succeeded him as regent. He quickly sidelined his cousin and heir-apparent al-Mufawwid; when al-Mu'tamid died in October 892, he succeeded to the throne. Like his father, al-Mu'tadid's power depended on his close relations with the army. These were first forged during the campaigns against the Zanj and were reinforced in later expeditions which the Caliph led in person: al-Mu'tadid would prove to be the most militarily active of all Abbasid caliphs. Through his energy and ability, he succeeded in restoring to the Abbasid state some of the power and provinces it had lost during the turmoil of the previous decades. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured picture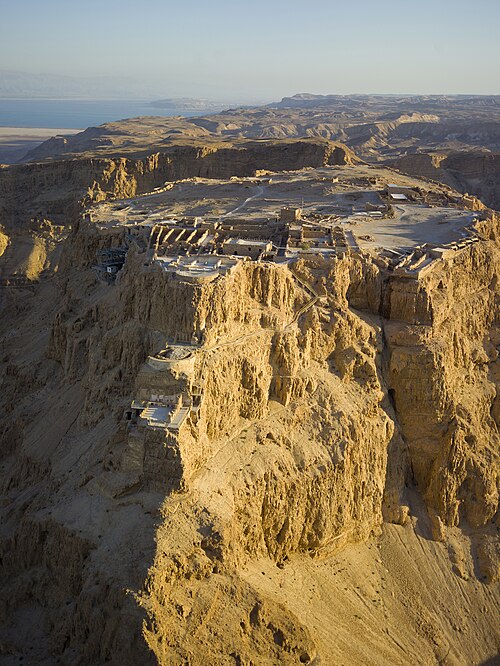 Credit: Photograph: Andrew Shiva An aerial view of Masada, an ancient fortification in the Southern District of Israel. Found atop an isolated rock plateau, it overlooks the Dead Sea. The first fortifications on the mountain were built by Alexander Jannaeus, and significantly strengthened by the Roman client king Herod between 37 and 31 BCE. During the First Jewish–Roman War of 66–73 CE, the fortress was besieged, falling only after the 960 Sicarii defending it committed mass suicide.
Masada is among the more popular tourist attractions in Israel, and in 2001 it was made a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
A panoramic view of the Hiroshima Peace Memorial, the site of the first atomic bomb to be used in warfare on August 6, 1945, during the final stages of World War II. Over 70,000 people were killed immediately, and another 70,000 suffered fatal injuries from the radiation, after the U.S. Army Air Force bomber Enola Gay dropped the bomb, codenamed "Little Boy". The Genbaku ("A-bomb") Dome (center) was directly beneath the blast, but managed to survive mostly intact. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsDiscover Wikipedia using portals Shortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |
How Can We Help?
































































































Recent Comments