Technetium (99mTc) exametazime is a radiopharmaceutical sold under the trade name Ceretec, and is used by nuclear medicine physicians for the detection of altered regional cerebral perfusion in stroke[1] and other cerebrovascular diseases. It can also be used for the labelling of leukocytes to localise intra-abdominal infections[2] and inflammatory bowel disease.[3] Exametazime (the part without technetium) is sometimes referred to as hexamethylpropylene amine oxime or HMPAO, although correct chemical names are:[4]
- (NE)-N-[(3R)-3-[[3-[[(2R,3E)-3-hydroxyiminobutan-2-yl]amino]-2,2-dimethylpropyl]amino]butan-2-ylidene]hydroxylamine
- or 3,3'-((2,2,-dimethyl-1,3-propanediyl)diimino)bis-2-butanone dioxime.
Chemistry
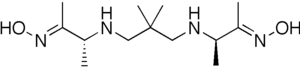
The drug consists of exametazime as a chelating agent for the radioisotope technetium-99m. Both enantiomeric forms of exametazime are used—the drug is racemic.[5] The third stereoisomer of this structure, the meso form, is not included.
References
- ^ Moretti JL, Defer G, Cinotti L, Cesaro P, Degos JD, Vigneron N, et al. (1990). ""Luxury perfusion" with 99mTc-HMPAO and 123I-IMP SPECT imaging during the subacute phase of stroke". European Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 16 (1): 17–22. doi:10.1007/BF01566007. PMID 2307169. S2CID 11934803.
- ^ Weldon MJ, Joseph AE, French A, Saverymuttu SH, Maxwell JD (October 1995). "Comparison of 99m technetium hexamethylpropylene-amine oxime labelled leucocyte with 111-indium tropolonate labelled granulocyte scanning and ultrasound in the diagnosis of intra-abdominal abscess". Gut. 37 (4): 557–64. doi:10.1136/gut.37.4.557. PMC 1382910. PMID 7489945.
- ^ Ui K, Yamaguchi T (December 1991). "[Therapy and diagnosis of emergency shock patients]". Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. The Journal of the Japanese Society of Internal Medicine. 80 (12): 1892–6. doi:10.2169/naika.80.1892. PMID 1804909.
- ^ "Exametazime". PubChem. National Institutes of Health.
- ^ "Monography in the European Pharmacopoeia" (PDF).
External links
- European Association of Nuclear Medicine: Ceretec
- GE Healthcare: Ceretec
- Exametazime ligand: CID 9552071 from PubChem


Recent Comments