How Can We Help?
You are here:
< Back
Chemical compound
Dacemazine (INN, also known as Ahistan and Histantine)[1] is a phenothiazine derivative which acts as a histamine antagonist at the H1 subtype. First described in 1951, it was never marketed as a drug on its own, although a combination of dacemazine and di-tert-butylnaphthalenesulfonate was sold as an antispasmodic and antitussive under the trade name Codopectyl.[1] It was also assessed as a possible anticancer drug.[2]
Synthesis
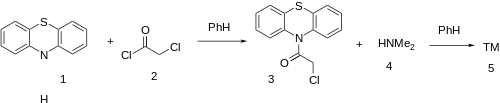
Amide formation between phenothiazine (1) and chloroacetyl chloride (2) gives 10-(Chloroacetyl)-phenothiazine [786-50-5] (3). The subsequent displacement of the remaining halogen with dimethylamine (4) completes the synthesis of dacemazine (5).
References
- ^ a b Triggle DJ, Ganellin CR, MacDonald F (1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. Vol. 1. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC. p. 711. ISBN 0-412-46630-9. Retrieved on August 2, 2008 through Google Book Search.
- ^ Karolyhazy G, Havas I, Jansco G, Kapas L, Sellei C (August 1952). "[The anticarcinogenic effect of dimethylaminoacetyl-phentiazide (ahistan)]". Kiserletes Orvostudomany (in Romanian). 4 (4): 260–2. PMID 13023855.
- ^ Dahlbom, Richard; Ekstrand, Torsten; Rubin, Inger; Saluste, E.; Stjernholm, R.; Ehrensvärd, G. (1951). "10-Aminoacylphenothiazines. I. Aminoacetyl and Aminopropionyl Derivatives." Acta Chemica Scandinavica. 5: 102–114. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.05-0102.
- ^ Wassermann, N. et al, Rev. Chim., 1959, 10, 81 (synth) (only until 1991)
- ^ Kano; Makisumi Shionogi Kenkyusho Nenpo, 1957 , # 7 p. 511,514 Chem.Abstr., 1958 , p. 10094.
- ^ John W. Cusic, U.S. patent 2,694,705 (1954 to G. D. Searle & Co.).
| H1 |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 |
| ||||
| H3 |
| ||||
| H4 |
| ||||
| Classes | |
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Anticholinergics | |
| Others |
|
Categories
-
Annuals36
-
Bulbs, Corms & Tubers41
-
Ferns27
-
Fruits3
-
Garden Plants23
-
Grasses26
-
Herb17
-
Insects1
-
Mammals1
-
Midwest Native Plants0
-
Northeast Native Plants112
-
Perennials123
-
Rose1
-
Shrubs47
-
Trees112
-
Tropical Plants53
-
Upland Birds5
-
Vines18
-
Viola Tricolor1
-
Water Gardening & Plants9
-
Waterfowl0
-
Wetland Birds0
-
Wetland Plants4
-
Wildbirds172
-
Wildflowers1
-
Woodland Plants29
Table of Contents


Recent Comments